Gastric Bypass: Procedure, Outcomes & Implications

Intro
Gastric bypass surgery has emerged as a significant intervention in the fight against obesity. Understanding this procedure is crucial for healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients alike. This surgery not only alters the gastrointestinal tract but also impacts various aspects of health and lifestyle. Insights into the mechanisms behind gastric bypass, its eligibility criteria, and the potential outcomes provide context to its role in managing obesity.
This section sets the stage for a more detailed exploration of the procedure, the implications it carries, and the psychological and physiological consequences for patients. It also emphasizes the importance of dietary strategies and psychological support during the entire process.
Preamble to Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypass surgery plays a significant role in the treatment of obesity, a condition that has reached epidemic levels worldwide. As a means of weight management, gastric bypass not only assists individuals in losing weight but also contributes to the improvement of various associated health conditions. This introduction lays the foundation for understanding the intricate details involved in gastric bypass procedures, outcomes, and the broader implications for patient health.
Defining Gastric Bypass
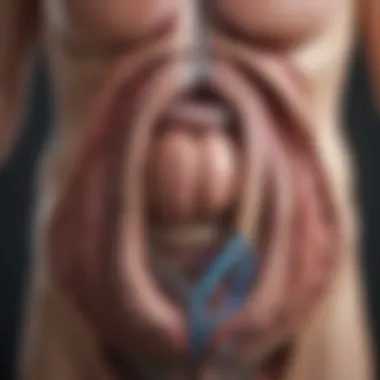
Gastric bypass is a surgical procedure used to promote weight loss by changing how the stomach and small intestine handle food. The surgery works by creating a small pouch in the stomach, which decreases the amount of food one can consume at a time. This pouch is then connected directly to the small intestine, bypassing a significant portion of the stomach and part of the intestine. This alteration not only restricts food intake but also reduces calorie absorption. There are different techniques for achieving this, including Roux-en-Y and Mini Gastric Bypass, each with subtle differences in execution and results.
This definition is fundamental, as it frames the entire discussion around gastric bypass. Recognizing what the procedure entails is essential for grasping the subsequent discussions on its mechanisms, eligibility, and the potential health outcomes associated with it.
Historical Context
The origins of gastric bypass surgery date back several decades. Initially introduced in the 1960s, it has evolved from a rudimentary procedure to a sophisticated surgical intervention available today. In the early days, bariatric surgeries were mainly experimental and viewed with skepticism due to high risks and complications. However, advancements in surgical techniques and technologies, including laparoscopic approaches, have greatly enhanced the safety and efficacy of the procedure.
Over the years, research has illuminated the relationship between obesity and various health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. This body of evidence led to a growing acceptance of gastric bypass as a legitimate treatment for obesity. Today, gastric bypass is recognized not just as a weight-loss method but also as a pivotal intervention that can significantly improve overall health outcomes for those struggling with obesity-related comorbidities.
Understanding this historical backdrop highlights the transformative nature of gastric bypass surgery and sets the stage for discussions about its relevance in modern medicine.
Mechanism of Action
Understanding the mechanisms behind gastric bypass surgery is crucial. These mechanisms not only explain how the procedure leads to weight loss but also offer insights into the physiological and psychological changes patients experience afterward. This section delves into surgical techniques and physiological changes post-surgery, ensuring a holistic understanding of the treatment's implications and outcomes.
Surgical Techniques
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass is one of the most common methods of performing gastric bypass surgery. This technique involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine. The key characteristic of this approach is that it involves both restriction and malabsorption. It reduces food intake while also causing food to bypass a significant portion of the intestine.
The Roux-en-Y technique is beneficial because it often results in significant weight loss and substantial improvement in metabolic diseases like Type 2 diabetes. A unique feature of this method is the alteration of gut hormones that influence hunger and satiety. However, patients must be vigilant about nutritional intake post-surgery to avoid deficiencies.
Mini-Gastric Bypass
Mini-Gastric Bypass presents a simpler surgical alternative. Similar to Roux-en-Y, this method creates a smaller stomach pouch and connects it to the intestine. The main characteristic of Mini-Gastric Bypass is its shorter operative time and reduced complication risk when compared to traditional methods.
This procedure is increasingly popular due to its effectiveness in achieving weight loss with fewer surgical steps. However, it has a higher potential for nutritional deficiencies since it bypasses even more of the intestines, requiring patients to be diligent about monitoring their nutritional status and supplementing accordingly.
Open vs. Laparoscopic Techniques
The choice between open and laparoscopic techniques plays a significant role in the surgical process. Open surgery involves a larger incision and may allow for better visualization of the surgical field. However, it usually comes with a longer recovery time and increased pain post-operation.
Laparoscopic techniques, on the other hand, utilize small incisions and camera guidance. This minimally invasive approach results in reduced recovery times, less postoperative pain, and smaller scars. The popularity of laparoscopic approaches is growing because of these advantages, yet it demands a surgeon with specific skills and experience in minimally invasive surgery.
Physiological Changes Post-Surgery
Post-operative physiological changes are considerable. These changes influence not only weight loss but also overall health and well-being.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes after gastric bypass surgery are significant. The procedure causes alterations in hormones such as ghrelin and leptin, affecting hunger and satiety. Ghrelin, which stimulates appetite, typically decreases, while leptin levels can increase, promoting feelings of fullness. This adjustment in hormone levels supports successful long-term weight loss.
Such changes contribute to improving metabolic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure. However, patients must understand that the emotional and psychological factors related to these hormonal changes can also influence their food choices and eating behaviors, making ongoing support important.
Nutrient Absorption
Nutrient absorption becomes a concern due to the bypassing of parts of the intestine. After surgery, the body may struggle to absorb essential nutrients, leading to potential deficiencies, especially in vitamins such as B12, iron, and calcium.
The capacity for nutrient absorption diminishes significantly in some patients, making proper monitoring and supplementation crucial. Nutritionists play a vital role in guiding patients on necessary dietary adjustments and helping manage any deficiencies that may arise. Thus, understanding nutrient absorption in this context is key to ensuring the long-term success of the procedure.
Eligibility Criteria
Understanding the eligibility criteria for gastric bypass surgery is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. It serves as a guideline to determine who may benefit the most from the procedure. A well-defined eligibility framework ensures that surgical interventions are performed on individuals whose conditions align with the expected outcomes. This leads to improved patient safety and satisfaction.
Body Mass Index Thresholds
Body Mass Index, or BMI, is a critical factor in evaluating eligibility for gastric bypass. Typically, a BMI of 40 or greater indicates severe obesity, while a BMI of 35 to 39.9 may also qualify if accompanied by obesity-related comorbidities. These thresholds help establish a common standard for assessing the potential success of the surgery.
This evaluation does not solely hinge on weight; it considers additional factors, such as the patient's overall health, age, and eating habits. Candidates who meet these BMI requirements often show a history of failed weight loss attempts through non-surgical methods, marking them as suitable for surgical intervention.
Comorbid Conditions
Comorbid conditions play a significant role in the assessment process for gastric bypass eligibility. Certain illnesses heighten the risks associated with obesity and can improve following surgery.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a leading comorbidity associated with obesity. Many individuals with obesity face challenges in managing their blood sugar levels, which can lead to various complications. By undergoing gastric bypass, patients often experience significant weight loss, which directly contributes to improved insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control.
One key characteristic of diabetes is its potential to be reversed through lifestyle changes following bariatric surgery. Studies show that many patients see remission of type 2 diabetes, reducing the need for medication. This makes the discussion of diabetes particularly relevant in the context of gastric bypass. The advantages include not only improved metabolic health but also a potential reduction in the risk for cardiovascular events.
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases are another common comorbidity linked with obesity. Conditions such as hypertension and heart disease place individuals at increased risk during surgery and in everyday life. Evidence indicates that weight loss through gastric bypass can lead to decreased blood pressure and improved cholesterol levels.
The critical characteristic here is the profound effect of weight loss on overall heart health. Many patients report improved exercise tolerance and a greater sense of well-being after surgery. This makes cardiovascular diseases a focal point in the evaluation of eligibility, emphasizing the necessity for intervention in this population.
In summary, when determining eligibility for gastric bypass surgery, the interplay of BMI thresholds and comorbid conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases creates a comprehensive framework. This ensures that individuals who are likely to receive the most benefit from the surgery are prioritized.
The Pre-Operative Process
The pre-operative process is a critical phase in the journey of gastric bypass surgery. It ensures that both the surgeon and the patients are prepared for the procedures ahead. This stage requires careful evaluation, planning, and education that fosters optimal outcomes. Understanding these elements can significantly shape the overall experience and effectiveness of the surgery.


Assessment and Evaluation
Medical History Review
The medical history review is the first step in ensuring that a patient is an appropriate candidate for gastric bypass surgery. This process involves outlining the individual’s past medical issues, current health status, and previous treatments. By understanding a patient's medical background, healthcare providers can identify potential risks and necessary precautions.
A key characteristic of medical history review is its thoroughness. It not only examines surgical history but also assesses conditions like hypertension or sleep apnea, which are relevant to surgical success. The detail in this review is beneficial as it provides insight into the patient's readiness for surgery.
One unique feature of the medical history review is its role in establishing a risk profile. Identifying past complications or conditions allows for tailored surgical approaches. However, challenges can arise if patients are not fully forthcoming about their medical history, which can impact surgical decision-making and outcomes.
Psychological Assessment
Psychological assessment is another essential component of the pre-operative process. This evaluation looks into emotional health and coping mechanisms, which are crucial for post-operative success. Understanding mental health is vital since weight loss surgery can bring on significant life changes.
A prominent aspect of psychological assessment is its focus on behavioral patterns. Identifying any eating disorders, anxiety, or depression can help in planning adequate support systems. This aspect is popular as it emphasizes the mental wellness aspect of the surgical journey.
One unique feature of psychological assessments is how they can lead to individualized care plans. This tailored approach is advantageous, ensuring that the emotional needs of the patient are met. Despite its benefits, conducting these assessments can sometimes be challenging due to patients being reluctant to discuss sensitive issues, which can obscure an accurate evaluation.
Preparing for Surgery
Dietary Changes
Dietary changes are fundamental in the pre-operative phase of gastric bypass surgery. Adapting one's diet helps prepare the body for significant physiological changes post-surgery. This approach often includes starting a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet which aids in weight reduction before the operation.
The key characteristic of dietary changes is their immediacy. These dietary adjustments significantly contribute to better surgical outcomes and faster recovery. Patients often find this aspect beneficial, as it fosters engagement with their health journey and prepares them psychologically.
A unique feature of dietary changes is their role in limiting liver size before surgery. This can make the surgical procedure easier and reduce complications. However, adjustments can pose a challenge for those who are unaccustomed to dietary restrictions, sometimes leading to frustration or confusion.
Medication Adjustments
Medication adjustments represent another important action in the pre-operative journey. Many patients take medications for various conditions, and evaluating these pre-surgery is crucial. Certain medications may need to be paused or altered to avoid complications during surgery.
The characteristic of medication adjustments is their focus on safety. This process is beneficial as it can prevent adverse reactions during surgery, thereby enhancing overall safety. Patients are often educated on the significance of timely adjustments, which empowers them in their care.
One unique aspect of medication adjustments is that it can dictate how well the body responds to surgery. For example, managing blood thinners is vital to reduce bleeding risks. However, navigating medication changes can also present challenges, as patients may experience anxiety regarding altering their routine.
Surgical Procedure
The surgical procedure for gastric bypass is a significant aspect of this article. It represents a critical milestone in the treatment of obesity and its related ailments. Understanding this process is vital for patients and healthcare professionals alike. By discussing the intricacies of the procedure, the reader can grasp its benefits, risks, and overall impact on patient health.
Step-by-Step Overview
The gastric bypass procedure typically involves several key steps. First, the surgeon makes a small incision in the abdomen. In many cases, this is done laparoscopically, which minimizes recovery time and scarring. Subsequently, the stomach is divided into a small upper pouch and a larger lower section. This change drastically reduces food intake.
Next, the small intestine is rearranged to connect to the pouch. This modification alters the digestive process. It enables the food to bypass a significant portion of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine. This procedure, known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is the most common surgical method used today.
Post-surgery, patients are often monitored closely to ensure stable recovery. The effectiveness of the procedure can be attributed to both reduced caloric intake and changes in digestion, leading to significant weight loss.
Anesthesia Considerations
Anesthesia plays a crucial role in the success of the gastric bypass procedure. Before surgery, patients undergo an evaluation to determine their suitability for anesthesia. Some individuals may have increased risks associated with general anesthesia due to pre-existing health conditions. This evaluation includes assessing airway stability, cardiac function, and respiratory health.
During the procedure, general anesthesia is typically administered. This ensures that the patient is completely unconscious and pain-free throughout the surgery. The choice of anesthetics and the method of administration are tailored to the patient's medical status and the surgical approach.
Post-anesthesia care involves careful monitoring to manage potential side effects. Patients often experience drowsiness and may require assistance during the recovery phase. Addressing these considerations beforehand can significantly improve surgical outcomes and enhance patient safety.
Post-Operative Care
Post-operative care is a critical phase in the gastric bypass journey. The success of this surgical intervention is significantly influenced by how well patients are supported during recovery. Proper care after surgery minimizes complications, enhances recovery time, and aids in achieving long-term successful outcomes.
Immediate Aftercare
Immediate aftercare begins in the hospital setting and usually lasts for a few days post-surgery. After the procedure, patients are closely monitored to ensure vital signs are stable. Medical staff checks for any signs of complications, such as infection or excessive bleeding. Pain management is also prioritized, as discomfort is common post-surgery.
Patients will typically start with clear liquids before progressing to full liquids. This gradual reintroduction of food helps the digestive system adjust to the new configuration.
- Monitoring vital signs
- Administering medications for pain management
- Providing education on nutrition and diet
Important instructions are given regarding activity levels. Doctors often recommend avoiding heavy lifting and rigorous physical activities until the body heals sufficiently. Patients are encouraged to walk short distances to promote circulation, which helps in preventing blood clots.
Long-Term Monitoring
Long-term monitoring is essential for maintaining health after gastric bypass. This phase often involves regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals. These visits typically focus on nutritional assessments, weight management, and psychological health.
- Nutritional Assessments: Regular check-ups help monitor for nutritional deficiencies, including vitamins and minerals that might be lacking due to altered absorption.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. Healthcare providers will help patients set reasonable goals and adjust meal plans as necessary.
- Psychological Health: Emotional support remains important. Many patients benefit from counseling or support groups. Adjustments to body image can be significant, and professional guidance can help.
Long-term success requires commitment and collaboration between patient and healthcare team.
Conclusively, effective post-operative care significantly contributes to the physical and emotional well-being of gastric bypass patients. Understanding the significance of immediate and long-term monitoring helps individuals to maximize the benefits of their surgery.
Expected Outcomes
The expected outcomes of gastric bypass surgery are critical to understanding its role in obesity treatment. Properly managed, these outcomes facilitate recovery, improve health, and enhance the quality of life. This section delves into the various results that can be anticipated following the procedure. These are not merely statistics; they reflect the profound changes patients endure and can direct future medical strategies.
Weight Loss Results
Initial Weight Loss
Initially, weight loss post-gastric bypass is often dramatic. Many patients experience significant reductions in body weight shortly after the procedure. This immediate result is defined by its high impact, often bringing about swift improvements in physical and mental health. It is a defining characteristic of the surgery, contributing to its popularity. Patients frequently report feeling physically lighter and more energized, which encourages further lifestyle changes.
The unique feature of initial weight loss lies in the motivation it provides. Patients often find this rapid change to be encouraging as it builds their confidence. However, it is also essential to note that this initial weight loss phase must be managed carefully. There are potential disadvantages, including nutritional deficiencies if dietary guidance is not followed.
Maintenance Strategies
Maintenance strategies for weight loss become crucial as patients transition from the initial phase. These strategies focus on sustaining the weight loss achieved in the first months. A key characteristic of maintenance is its requirement for continuous effort and commitment from patients. It is essential for preventing weight regain, which can happen if old habits resurface.
One well-known approach includes regular engagement with a dietitian and participation in support groups. These ongoing connections offer accountability, helping to instill long-term healthy eating habits. The advantage of a structured maintenance plan is its potential to provide lasting results. Nonetheless, every patient faces the challenge of adapting to these new lifestyle modifications, which can be a continuous source of stress as they work to avoid the pitfalls of past routines.

Health Improvements
Resolution of Comorbid Conditions
The resolution of comorbid conditions is one of the most compelling advantages of gastric bypass. Many patients find that conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea significantly improve or even resolve after surgery. This aspect not only enhances the quality of life but also tends to reduce healthcare costs for ongoing treatment of these conditions.
The unique aspect of this resolution is that it underscores the surgery's dual role. Gastric bypass is not just a weight loss tool; it also serves as a means of improving general health. For many, this can mean a newfound freedom from medications and regular doctor visits associated with their earlier conditions. However, not every patient sees full resolution. Therefore, long-term monitoring of health conditions remains vital.
Enhancement of Quality of Life
The enhancement of quality of life following gastric bypass surgery cannot be overstated. Many patients report significant improvements in their subjective well-being after surgery. This includes increased mobility, improved mental health, and a generally greater sense of fulfillment in daily activities.
The hallmark of improved quality of life is the ability to participate in social and physical activities that were previously difficult or impossible. Patients often enjoy newfound confidence and heightened self-esteem. It leads to better relationships and engagement with family and friends.
However, the emotional journey might still pose challenges. Patients may need psychological support to help adjust to their new self-image and lifestyle. Overcoming old habits and mindsets is a unique feature of recovery that requires ongoing effort and support.
"Gastric bypass surgery serves not only as a pathway to weight loss but also a significant turning point in health and lifestyle for many individuals."
Complications and Risks
Understanding the potential complications and risks associated with gastric bypass surgery is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. This section aims to clarify these issues by outlining common complications, as well as psychological considerations that may arise following surgery. Addressing these concerns is vital not only for patient safety but also for ensuring that individuals have realistic expectations about their journey after surgery.
Common Complications
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies are a significant aspect of the post-operative phase for patients undergoing gastric bypass. This occurs when the body does not absorb enough vitamins and minerals due to the altered digestive process. For instance, deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, and calcium are commonly observed. This is an important choice for this article because addressing nutritional deficiencies can influence overall health and recovery rates.
Patients must be educated on proper supplementation and dietary adjustments to mitigate these risks. The unique feature of nutritional deficiencies is that they can lead to serious health issues, including anemia and weakened bones, if left unaddressed. A proactive approach, including regular blood tests and tailored nutritional plans, can greatly enhance patient outcomes post-surgery.
Dumping Syndrome
Dumping syndrome is another potential complication that some patients may experience after gastric bypass. It is characterized by rapid gastric emptying, which leads to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, often after eating. This condition is a prevalent subject in this article since understanding its causes can help patients modify their eating habits to prevent its occurrence.
One unique feature of dumping syndrome is the way it can affect food choices; patients might lean towards low-sugar and low-fat meals to reduce symptoms. The advantages of recognizing this syndrome lie in the proactive adjustments patients can make to their diets, thus enhancing their quality of life and overall satisfaction with the surgery results.
Psychological Considerations
Body Image Issues
Body image issues can significantly impact patients after gastric bypass surgery. Facing dramatic changes in physical appearance can lead to feelings of inadequacy or anxiety. This aspect is crucial for this article because it emphasizes the emotional challenges that may arise alongside physical transformations.
A key characteristic of body image issues is that they do not resolve automatically following surgery. The unique feature here is the need for psychological support and counseling post-surgery to help individuals adapt to their new identity. By providing a space for discussion and reflection, patients can foster a healthier relationship with their bodies over time.
Pre-existing Mental Health Conditions
Pre-existing mental health conditions can complicate the post-operative journey for gastric bypass patients. Conditions such as depression or anxiety can exacerbate after surgery due to various changes in lifestyle, including dietary restrictions and social interactions. This area is another beneficial focus for this article as it highlights the need for comprehensive psychological screening prior to surgery.
A vital element of this topic is understanding how these conditions can influence recovery and weight loss outcomes. The unique challenge is that mental health must be continuously monitored and supported, ensuring patients receive the holistic care needed for success. Coordination between surgeons, dietitians, and mental health professionals can foster a supportive environment that addresses these complexities.
"Understanding the complexities of complications and psychological impacts can enhance the care patients receive, paving the way for better outcomes in their post-operative journey."
Nutritional Management
Nutritional management is a critical aspect of the gastric bypass journey. It focuses not only on what patients eat post-surgery but also on how they adapt their dietary habits to support their health and weight loss goals. This section delves into dietary requirements that patients must follow and the long-term eating habits necessary for achieving sustainable results.
Dietary Requirements
Post-Surgery Dietary Phases
The post-surgery dietary phases are designed to facilitate recovery while ensuring that the patient receives essential nutrients. Immediately after surgery, patients begin with a clear liquid diet. This phase lasts about one week. Progressing gradually is crucial, as it allows the body to adjust without overwhelming it.
A key characteristic of this phase is the introduction of soft foods after the clear liquids. Foods like mashed potatoes and yogurt come into play. The careful transition helps reduce discomfort and supports healing. It is a beneficial choice as it minimizes stress on the newly formed stomach pouch. The unique feature is that this progression is monitored, emphasizing individual comfort and health needs.
However, it has disadvantages; some patients may struggle with specific foods and need adjustments. Monitoring is essential to manage these challenges and ensure a positive experience.
Supplementation Needs
Supplementation needs arise as patients may have reduced nutrient absorption post-surgery. Vitamins and minerals like vitamin B12, iron, and calcium are often required. These supplements are vital for preventing deficiencies that can occur due to the changes made to the digestive system.
A key characteristic of supplementation is its tailored approach. Patients receive specific recommendations based on their dietary habits and blood test results. It is a popular choice for maintaining health and wellness post-surgery. The unique element of supplementation needs is the personalization according to individual nutrient levels observed during follow-ups. While this is advantageous, patients must remain vigilant about adhering to the supplement schedule. Missing doses can lead to serious health complications, making education about these needs crucial.
Long-Term Eating Habits
Long-term eating habits take shape as patients adjust to life post-gastric bypass. Eating becomes a deliberate process focusing on nutrient-dense foods rather than volume. Emphasizing high protein intake, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates will better support weight loss and health improvements.
Regular meal timing aids metabolism and fosters routine. Many patients also find it advantageous to incorporate smaller meals, promoting a steady energy level throughout the day. Mindful eating practices are essential to help recognize hunger cues and prevent overeating.
Adhering to these long-term habits is important for maintaining weight loss and preventing weight regain. Routine follow-ups often provide extra guidance and evaluation ensuring individuals stay on track with their nutritional goals.
"After gastric bypass, nutrition is not just about choosing healthy foods; it is a continuous learning and adapting process that can significantly impact overall life quality."
Nutritional management in the context of gastric bypass thus becomes an ongoing, structured, and adaptive journey, essential in achieving sustainable health and weight loss goals.
Psychological Support
Psychological support plays a crucial role in the journey of individuals undergoing gastric bypass surgery. The transition into a new lifestyle after the operation necessitates not only physical adjustments but also emotional and mental resilience. Patients often confront various psychological challenges before and after the procedure, making support systems an essential aspect of recovery and long-term success.
A comprehensive approach to psychological support includes counseling opportunities and participation in support groups. Both are key elements that help patients navigate their emotions, expectations, and behaviors. This section delves into the significance of these support structures.
Counseling Opportunities
Counseling can offer valuable insights for gastric bypass patients. One-on-one sessions with trained professionals provide a safe space for individuals to express their concerns and fears regarding the surgery. These sessions often focus on several important areas:
- Behavior Modification: Therapists assist patients in identifying and changing unhealthy eating patterns. This is crucial for long-term success post-surgery.
- Coping Strategies: Many patients experience anxiety or depression. Therapy can equip them with tools to manage these feelings effectively.
- Goal Setting: Setting realistic and achievable goals is vital. Counselors help in formulating plans that resonate with the patient’s lifestyle and aspirations.
- Motivation Maintenance: Maintaining motivation is difficult over time. Ongoing counseling reinforces commitment to the new lifestyle, helping to combat disillusionment or fatigue.
For those considering gastric bypass surgery, seeking counseling in advance can provide the foundational support that promotes readiness for change and success after the operation.


Support Groups
Support groups offer an alternative avenue for psychological support among gastric bypass patients. These groups are invaluable as they build community and foster shared experiences. Participating in a support group has several benefits:
- Community Connection: Engaging with others who have similar experiences can help alleviate feelings of isolation that may arise post-surgery.
- Shared Knowledge: Group members often share tips, strategies, and experiences that can be beneficial in managing post-operative life. Learning from others can inspire and guide individuals in their journey.
- Emotional Outlet: These groups provide a platform for members to voice their struggles and achievements, creating a sense of belonging.
- Accountability: Regular meetings encourage accountability among group members, fostering commitment to lifestyle changes.
Remember, every journey is unique. Engaging with psychological support structures can make a substantial difference in navigating the path to health and wellness.
Impact on Lifestyle
The impact of gastric bypass surgery on lifestyle cannot be underestimated. It represents not only a surgical treatment for obesity but also a fundamental shift in daily habits and routines for the patient. After undergoing the procedure, individuals often need to navigate a new way of living that emphasizes health, nutrition, and physical activity. This section focuses on several important elements, including physical activity recommendations and the social dynamics that can change after surgery.
Physical Activity Recommendations
Engaging in physical activity post-surgery is crucial for achieving and maintaining weight loss. Patients are often encouraged to gradually increase their level of activity. Initially, simple activities like walking can be beneficial. As the body heals and strength returns, incorporating more intensive exercises such as strength training or aerobic workouts becomes advisable.
Some recommendations include:
- Start Slow: Begin with light activities and progressively build up. This prevents injury and discourages burnout.
- Aim for Regular Activity: Patients should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly, such as brisk walking or swimming.
- Incorporate Variety: It may be helpful to include different types of exercises to prevent monotony. This could involve cycling, dancing, or classes that focus on flexibility and strength.
"Physical activity enhances overall well-being and boosts the capacity for weight management post-surgery."
These adjustments in physical activity are not just about increasing calorie expenditure; they are also pivotal in improving mental health. Increased activity levels can help reduce anxiety and depression, which may affect some individuals after surgery. Thus, creating a routine that includes physical activity is as much about psychological benefits as it is about physiological gains.
Social Dynamics Post-Surgery
Social dynamics can shift substantially following gastric bypass surgery. Individuals may find that their interactions with family, friends, and colleagues change as a result of their weight loss journey. This can lead to a mix of positive and negative experiences. Understanding these shifts is essential for navigating new social landscapes.
- Support Networks: Many find that they draw closer to support groups related to weight loss. Engaging with others who have undergone similar experiences can provide valuable emotional backing and encouragement.
- Change in Relationships: Existing relationships can change as well. Some friends may not be supportive of the lifestyle changes, while others might celebrate and encourage them. This variability can lead to feelings of isolation or increased support; thus, it is crucial to build a network that truly supports one's health journey.
- New Social Norms: As people change their lifestyles, they often adapt new dietary and activity norms. Social outings may involve different choices, like opting for healthier menu items. This shift can alter group dynamics and peer influences.
In summary, the impact of gastric bypass on lifestyle is significant. Transitioning into a healthier lifestyle requires dedication to physical activity and an awareness of changing social dynamics. Patients who acknowledge and embrace these changes may find themselves achieving greater satisfaction and success in their weight loss journey.
Cost and Accessibility
Understanding the cost and accessibility of gastric bypass surgery is crucial for patients and healthcare professionals alike. Financial considerations can significantly affect a patient's decision to pursue this option for obesity treatment. The implications of surgery go beyond the operation itself, influencing ongoing health care, lifestyle changes, and overall quality of life.
Financial Considerations
Gastric bypass surgery can be an expensive endeavor. The total costs often include the surgical procedure, hospital stay, pre-operative assessments, and post-operative care. Some estimates show that the cost can vary between $20,000 to $35,000 depending on the hospital, geographical location, and the complexity of the procedure.
Patients should also consider additional expenses that may arise, such as:
- Medications: Prescriptions for pain management or supplementary vitamins may be necessary after surgery.
- Follow-up Care: Regular appointments to monitor weight loss and nutritional intake are also critical.
- Nutritional Support: Many patients require specialized dietary plans and possibly nutritional supplements to ensure proper recovery and maintain health.
Moreover, the financial impact should be evaluated against potential long-term savings from improved health. Weight loss can lead to a reduction in obesity-related conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, which may result in lower medical costs in the future. The potential for losing weight can also improve productivity and enhance quality of life, providing further justification for the initial investment.
Insurance Coverage
Insurance coverage for gastric bypass varies significantly. Not all plans cover the procedure, and regulations differ by location. Here are important points to consider regarding insurance coverage:
- Pre-Approval Requirements: Many insurance companies require documentation of medical necessity. This often includes proof of previous attempts to lose weight through diet and exercise.
- Network Providers: Patients may need to select surgeons and facilities that are part of their insurance plan’s network to receive full benefits.
- Out-of-Pocket Costs: Even with insurance, patients may still face high premiums, deductibles, or co-pays. Understanding how much will be out of pocket after insurance applies is essential.
It is also advisable to check the plan’s guidelines regularly, as coverage rules can change. Patients are encouraged to contact their insurance providers directly to obtain clear information regarding coverage specifics.
"Understanding costs and insurance coverage is vital for patients considering gastric bypass. It can influence their choices significantly, impacting long-term health journeys."
Patients should approach financial considerations with care, planning effectively to navigate through what can often be a complex landscape of surgical costs and insurance policies.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical considerations surrounding gastric bypass surgery are multifaceted. Understanding these aspects is crucial for healthcare providers, patients, and policymakers involved in the bariatric field. Ethical issues include patient autonomy, informed consent, and the long-term responsibilities of surgeons, among others.
One primary importance of discussing ethical considerations is to ensure that patients fully understand the operation they are contemplating. Gastric bypass is not merely a surgical procedure but also a significant lifestyle change. Patients must weigh the potential risks against benefits comprehensively. The ramifications extend beyond physical health, affecting mental, emotional, and social well-being, warranting a thoughtful dialogue.
Patient Autonomy
Patient autonomy refers to the right of patients to make informed decisions about their own medical treatment. It emphasizes the importance of involving patients in the decision-making process regarding gastric bypass surgery. Patients should have access to all pertinent information related to their options, risks, and expected outcomes. Surgeons play a critical role in upholding this autonomy by ensuring that patients receive comprehensive educational resources.
In practice, respecting patient autonomy means allowing patients to voice their concerns, preferences, and questions. Health care providers should encourage open discussions without coercing patients into any decisions. The informed consent process, therefore, becomes an essential ethical component. It should not only be a formality but a genuine exchange that empowers patients.
Challenges may sometimes arise, particularly when patients have pre-existing psychological conditions or may struggle to understand the complexities of their choices. In these cases, the healthcare team should provide additional support to facilitate understanding, ensuring that decisions are made based on a clear grasp of their implications.
Long-term Responsibilities of Surgeons
Surgeons have an ethical obligation towards their patients that extends beyond the operating room. Once a patient has undergone gastric bypass, the responsibility for maintaining the patient’s health continues. This includes ongoing monitoring of nutritional status, weight management, and addressing any complications that may arise post-surgery.
Moreover, surgeons should be cognizant of the long-term lifestyle modifications their patients will need to adopt. Post-operative care should encompass both physical and psychological aspects. Surgeons must advocate for comprehensive follow-up care, referring patients to dietitians and mental health professionals as necessary.
Maintaining open lines of communication between the patient and surgical team is paramount. Any issues should be addressed promptly to avoid deterioration of the patient’s health. This fosters trust and reinforces the ethical foundation of the surgeon-patient relationship.
"The journey of a patient does not end at the operating table; it continues through a lifetime of choices and challenges."
Future Directions in Bariatric Surgery
The field of bariatric surgery, particularly gastric bypass, is undergoing rapid evolution. The importance of examining future directions in bariatric surgery cannot be overstated. This section explores how technological advancements, procedural innovations, and improved patient care strategies may significantly alter the landscape of obesity treatment. Understanding these developments can enhance patient outcomes, making the surgical experience safer and more effective.
Emerging Techniques
New surgical techniques are constantly being developed to address not only the challenge of obesity but also its associated comorbid conditions. Some notable emerging techniques include the following:
- Single-incision laparoscopic surgery: This technique reduces recovery time and minimizes scarring by utilizing only one small incision. It offers a less invasive option compared to traditional methods, though it requires skilled surgeons.
- Endoscopic procedures: These are less invasive methods that involve tools inserted through the mouth and into the stomach. Examples include gastric balloon placement and sleeve gastroplasty, which may provide alternatives to more invasive surgeries like gastric bypass.
- Robotic-assisted surgeries: Robotics can enhance precision during surgery, potentially reducing complications and improving outcomes for patients. This technology allows for greater control and visibility, aiding surgeons in complex procedures.
These techniques highlight a shift toward minimally invasive procedures and improvements in surgical technology. The benefits are clear: shorter hospital stays, reduced pain, and faster recovery times.
Research on Long-term Outcomes
Continued research into the long-term outcomes of bariatric surgery is crucial. This area of study focuses on the durability of weight loss and overall health improvements post-surgery. Important aspects of this research include:
- Long-term effectiveness: Ongoing studies assess how effective gastric bypass remains over extended periods. Research shows that while initial weight loss can be significant, maintaining that loss is more variable.
- Comorbid condition management: Investigations into how surgical weight loss affects conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea are vital. Understanding these relationships helps refine patient selection for surgery and informs follow-up care protocols.
- Quality of life: The psychological and social aspects of undergoing weight loss surgery are also extensively studied. Research indicates many patients report improved quality of life post-surgery. Further studies aim to understand the factors that contribute to this improvement.
"Bariatric surgery stands at a turning point, with new techniques promising a more tailored approach to treatment. Research efforts are crucial for realizing the full potential of these advancements."
The focus on long-term outcomes is paramount. It can lead to more personalized care and improved surgical protocols. Furthermore, understanding long-term impacts supports better education for patients considering surgery. Together, emerging techniques and ongoing research present great promise for the future of bariatric surgery.



