Effective Strategies for Molluscum Contagiosum Treatment

Research Context
Background and Rationale
Molluscum contagiosum is more than just a skin condition; it's a viral infection that impacts individuals across various demographics. Primarily caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus, the resultant lesions—characterized by small, raised, and sometimes itchy bumps—pose unique challenges for both patients and healthcare providers. The frequency of this infection in children contrasts sharply with its occurrence in adults, where it often indicates underlying health concerns or weakened immune systems. This dichotomy shows how understanding the context of molluscum contagiosum is essential, paving the way for effective treatments.
Furthermore, the psychological ramifications of this viral condition cannot be overlooked. For many, skin ailments evoke feelings of embarrassment or shame, leading to social withdrawal. This underscores the necessity for comprehensive therapeutic approaches that not only address the physical symptoms but also consider the emotional and social implications for the affected individuals.
Literature Review
A significant body of research exists surrounding molluscum contagiosum, yet the clinical guidelines remain fragmented. Several studies have delved into treatment methodologies, examining their effectiveness and side effects. For instance, topical therapies like imiquimod and cantharidin have shown promise, while other more invasive interventions, like curettage, present differing results in terms of patient satisfaction and recurrence rates.
In addition to traditional medical approaches, literature emphasizing patient education is gaining traction. Understanding the natural progression of the infection and the various treatment modalities empowers patients, enabling informed decisions about their care.
Insight into emerging treatments, such as laser therapies and cryotherapy, opens up new avenues for discussion among professionals in dermatology and allied fields. Current trends indicate a move toward integrative approaches that combine established practices with novel strategies, fostering better outcomes and improved quality of life for those impacted by this infection.
Methodology
Research Design
The exploration of molluscum contagiosum treatments requires a multifaceted research design. Various methodologies—including qualitative reviews, randomized controlled trials, and observational studies—are crucial to glean a richer understanding of treatment efficacy.
In studies focusing on topical agents, for example, randomized controlled trials are employed to compare the effectiveness of imiquimod against placebo, providing robust data for clinicians. Meta-analyses further synthesize results from multiple trials, yielding a comprehensive overview of current approaches.
Data Collection Methods
Data collection is instrumental for articulating the nuances of treatment methodologies. Sources include:
- Clinical Trials: Monitoring patient outcomes through stringent protocols.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Gathering insights from patients regarding their experiences with various treatments.
- Medical Records: Analyzing historical data to track the effectiveness and recurrence rates of different interventions.
This combined approach allows for a thorough understanding of not just the 'what' of treatments, but the 'why' and the 'how.' Utilizing patient feedback enables an accurate reflection of the lived experience, which is vital not only for improving treatment strategies but also for tailoring recommendations based on individual patient needs.
"Patient understanding plays a key role in the success of any treatment. The more informed they are, the better the outcomes."
By piecing together findings from various research domains, this analysis aims to forge a path toward more effective and holistic treatment strategies for individuals grappling with molluscum contagiosum.
Intro to Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is more than just an innocuous skin condition; it presents a series of challenges that can greatly impact the quality of life for those affected. Understanding the intricacies of this viral infection is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers alike. The condition is not simply a nuisance; it plays a role in an individual's emotional and social well-being. In this section, we will dissect not only the clinical aspects of the infection but also the broader implications it carries within healthcare settings, emphasizing the necessity of effective treatment strategies.
Defining Molluscum Contagiosum
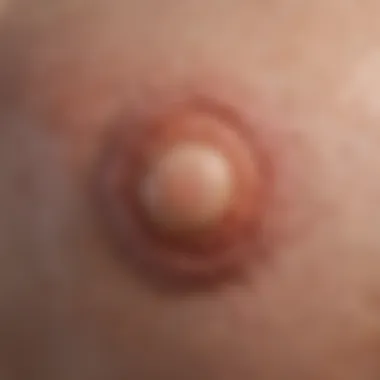
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a poxvirus and is primarily characterized by the appearance of small, raised, pale nodules on the skin. These nodules often have a central dimple and can range in size from 2 to 5 millimeters. While many skin maladies are attributed to external irritants or conditions, molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection that spreads through direct skin contact, making awareness and education vital. It's a common condition, especially among children, but it can also be found in adults, particularly those with a weakened immune system.
Epidemiology and Transmission
The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum is quite intriguing. It is prevalent worldwide, with currents studies pegging its incidence higher in children aged 1 to 10 years. While it’s generally benign, the way it spreads warrants attention. Common routes of transmission include:
- Direct contact: Skin-to-skin contact typically occurs in settings like playgrounds and locker rooms.
- Indirect contact: Virus particles can remain viable on surfaces; thus, shared towels or sports gear can facilitate its spread.
- Autoinoculation: Individuals can inadvertently spread the virus from one location on their body to another, complicating treatment efforts.
Clinical Presentation
Clinically, molluscum contagiosum exhibits unique features that make it relatively straightforward to diagnose. Given its propensity to create painless lesions, many affected individuals may not seek medical attention until lesions become visible. The lesions may persist for months and often resolve spontaneously; however, the psychological impact during this period shouldn't be minimized.
Most people don’t realize that while molluscum contagiosum is benign, its visibility can seriously affect self-image and cause social withdrawal.
In various cases, secondary bacterial infections can occur, particularly if the lesions are scratched or irritated. This aspect is essential to monitor as it can complicate the condition, subverting its benign nature into something more troublesome.
With this foundation laid, we can transition to examining treatment options in more depth, setting the stage for a comprehensive understanding of how to effectively manage molluscum contagiosum.


Understanding Treatment Options
Navigating through molluscum contagiosum treatment requires more than a basic understanding of the condition itself. With various treatment options available, knowing the best course of action plays a crucial role in the healing process. Each treatment type offers distinct benefits and potential drawbacks; thus, a comprehensive approach must take into account not only the medical aspects but also individual patient circumstances. Ultimately, understanding treatment options is about empowering patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions that can positively impact recovery outcomes.
Overview of Treatment Modalities
When it comes to tackling molluscum contagiosum, multiple treatment modalities come into play. This variety stems from the need to tailor interventions based on an individual’s circumstances, ranging from skin type to the extent of the infection. This can include:
- Topical Therapies: Such as Imiquimod, utilized to stimulate the immune response, or retinoids aimed at accelerating the skin cell turnover.
- Cryotherapy: A popular method employing extreme cold to destroy molluscum lesions. Patients often prefer it for its quick application.
- Curettage and Laser Therapy: Manual removal or laser ablation of lesions can be effective, though care and precision are needed in execution.
- Oral Medications: Antiviral agents, although less common, may be indicated in certain resistant cases or severe manifestations.
Each method brings its own set of advantages and challenges, and understanding these nuances allows for better choices to be made.
Factors Influencing Treatment Selection
In deciding the most appropriate treatment for molluscum contagiosum, various factors come into play that can shape the final choice.
- Patient Age and Health: Young children often face different treatment needs compared to adults. Their delicate skin may react more sensitively to certain therapies.
- Severity and Duration of Infection: More extensive and prolonged outbreaks might warrant aggressive treatments, while localized and recent infections may only require topical remedies.
- Personal Preferences: Some patients prefer non-invasive options, while others might opt for surgical methods based on their comfort levels.
- Accessibility and Cost: Insurance coverage and the affordability of specific treatments can significantly influence options. Sifting through this maze ensures effective treatment can be achieved without unnecessary financial burden.
In summary, understanding treatment options equips healthcare providers and individuals with the knowledge necessary for making informed decisions regarding molluscum contagiosum management, fostering more effective outcomes in management.
Deciding on a treatment isn't just picking one out of a hat; it's a thought-out process that integrates clinical knowledge and personal health considerations.
Molluscum Contagiosum Treatments
Molluscum contagiosum treatments encompass a variety of approaches tailored to address this common viral skin condition effectively. The treatment landscape frequently focuses on options that eliminate lesions and reduce transmission risk. Understanding the nuances of each treatment option is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike, especially since individual responses to therapy can significantly vary.
When managing molluscum contagiosum, considerations such as the patient’s age, immune status, and the severity of the infection can influence the choice of treatment. This section aims to detail various treatment modalities, providing insights into their strengths and disadvantages, helping guide those affected in choosing the most appropriate option.
Topical Therapies
Credé's solution
Credé's solution plays a pivotal role in molluscum contagiosum treatment. It's a topical antiseptic that utilizes silver nitrate as its active ingredient. This treatment is favored for its easy application and ability to effectively cauterize lesions. The potential benefits are clear, as the solution targets individual molluscum lesions without causing significant distress to surrounding skin.
However, a notable drawback lies in its potential to cause local irritation, which might deter some from continuous use. Yet, the power of Credé's solution to provide visible results makes it a popular choice among healthcare providers.
Imiquimod
Imiquimod is another topical medication often recommended for molluscum contagiosum. This immune response modifier works by stimulating the body's immune system to combat the virus causing the lesions. One of its standout features is its user-friendliness; the medication is self-applied at home, allowing for patient independence in managing their condition.
While many appreciate its ease of use, Imiquimod does come with its fair share of side effects such as local skin reactions, including redness and irritation. Even so, its effectiveness in treating molluscum contagiosum makes it a viable option in many treatment plans.
Retinoids
Retinoids, often recognized for their repertoire of skin benefits, can also be advantageous in molluscum contagiosum management. By promoting cell turnover and reducing keratinization around the lesions, retinoids can help expedite the healing process. They can be especially effective for patients with multiple lesions.
One noteworthy characteristic is their versatility; retinoids can enhance skin texture in addition to targeting molluscum. However, some users may experience dryness or irritation during use, which can be a deterrent. Balancing these effects with the benefits is key in determining their suitability for particular patients.
Cryotherapy
Mechanism of Action
Cryotherapy, or cryosurgery, employs extreme cold to destroy unwanted tissue, including molluscum lesions. The process involves applying liquid nitrogen to the lesions, freezing and ultimately eliminating the infected cells. The effectiveness of this approach is attributed to immediate destruction of the virus due to the sharp drop in temperature, making it a compelling option.
Despite its impressive mechanism, patient comfort during the procedure can vary. Some may find it uncomfortable, but the short duration of treatment often makes it bearable. The clarity in its action and perceived results make cryotherapy a favored choice among dermatologists.
Efficacy Assessment
Assessing the efficacy of cryotherapy involves understanding both immediate and long-term outcomes. Studies have demonstrated that many patients see complete lesion clearance within a few sessions. Cryotherapy is particularly beneficial for individuals with localized infections, although its result might differ in larger areas.


Patients might need multiple sessions, which can be seen as both an advantage and a limitation. However, the high success rate associated with cryotherapy often outweighs the concerns regarding frequency of treatments, making it a mainstay in molluscum contagiosum therapy.
Curettage and Laser Therapy
Procedure Description
Curettage involves the physical scraping of molluscum lesions, which is often followed by laser treatment to precisely target remaining cells. This dual approach allows for effective removal of larger or stubborn lesions. The procedure is conducted under local anesthesia, making it manageable for many patients.
One strong characteristic of this method is its immediate visibility of results; patients often notice significant improvements right after treatment. However, as with any invasive procedure, there's an associated risk of scarring, which healthcare providers must manage carefully with their patients.
Post-Treatment Care
Post-treatment care is an integral part of the recovery process following curettage and laser therapy. Patients may be advised on how to care for the treated area to prevent infection and promote healing. Moisturization and the use of topical antibiotics are commonly recommended.
The attention to post-treatment can greatly enhance the overall outcome, reducing the likelihood of complications. Informing patients about the importance of aftercare is essential in this regard, ensuring they are equipped to handle their recovery effectively.
Oral Medications
Antiviral Agents
Oral antiviral agents are sometimes utilized in managing molluscum contagiosum, particularly when topical therapies prove inadequate. These medications work to inhibit viral replication, thus reducing the viral load. One significant aspect of antiviral therapy is its systemic nature, which can benefit patients who have widespread lesions or are immunocompromised.
While the effectiveness of these agents can be undeniable, they often come with a range of potential side effects that warrant careful monitoring. Thus, it’s generally considered a second-line option unless clinically warranted.
Systemic Treatments
Systemic treatments for molluscum contagiosum include different formulations aimed at providing a comprehensive approach for tackling more persistent cases of the infection. This may involve long-term antiviral therapy or adjunct treatments targeting the immune system. The breadth of available systemic treatments offers pathways for those struggling with severe cases.
A drawback, however, is the potential for systemic side effects, which may necessitate more frequent check-ins with healthcare providers. Yet, for patients whose situations call for more aggressive management, such treatments can be life-changing.
Understanding the various treatment options enables better decision-making regarding molluscum contagiosum management. Each approach carries its unique attributes and considerations, paving the way for tailored solutions that address individual patient needs.
Natural History and Prognosis
Understanding the natural history and prognosis of molluscum contagiosum is crucial for managing expectations and guiding treatment decisions. The course of the disease can vary among individuals based on several factors, such as the immune response, age, and the area of the body affected. By comprehensively grasping the expected trajectory of the infection, healthcare professionals and patients can better navigate the available treatment options.
Expected Course of Disease
The expected course of molluscum contagiosum typically involves several phases. Initially, the infection may present as small, firm, raised bumps on the skin, often with a dimple in the center. Patients, particularly children, might experience a gradual increase in the number of lesions over weeks to months, with lesions typically persisting for about 6 to 12 months if left untreated. However, it’s important to note that the duration can be much longer in immunocompromised individuals.
- Lesion Progression: Often, these bumps can change in appearance, leading to a more significant lesion burden, which can heighten concern among patients about contagion.
- Spontaneous Resolution: Many cases resolve spontaneously, with the body's immune system eventually eliminating the virus. Some studies suggest that around 80% of lesions may clear up without any intervention within a couple of years, although this can be highly variable.
- Potential for Recurrence: Recurrences can happen, particularly in individuals with previous infections or those with weakened immune systems. Factors like high humidity or skin trauma can exacerbate the condition, prolonging the infection's course.
It's vital to consider that while many lesions resolve on their own, treatment may be necessary to alleviate symptoms or prevent the spread of the infection to others.
Potential Complications
While molluscum contagiosum is generally viewed as a mild condition, several potential complications can arise, particularly if lesions are left unattended. These complications can significantly affect a patient's quality of life.
- Secondary Bacterial Infections: One of the main concerns is the risk of secondary infections. Scratching or picking at the lesions can introduce bacteria, leading to impetigo or cellulitis, conditions requiring antibiotics.
- Dermatitis: In some cases, patients may develop dermatitis, an inflammatory skin condition, as a reaction to the virus itself or due to irritation from scratching. This can lead to itchiness, redness, and further complications.
- Psychological Impact: Additionally, the presence of visible lesions can have emotional and psychological implications, particularly in children and adolescents, leading to low self-esteem or social withdrawal.
The management of molluscum contagiosum goes beyond mere physical symptoms. Understanding its course and complications helps in developing a holistic approach that includes addressing emotional well-being.
Psychosocial Impact of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is not just a physical ailment; it carries a weight of psychosocial implications that can be profound and lasting. Understanding how this viral skin infection affects an individual on emotional and social levels is crucial for achieving a holistic approach to treatment.
The significance of evaluating the psychosocial impact cannot be overstated. Patients often find themselves grappling not just with the physical symptoms of molluscum contagiosum but also with anxiety about their appearance and the reactions of others. This can lead to a myriad of issues, including decreased self-esteem, social withdrawal, and challenges in professional or academic environments. Addressing these concerns alongside the physical treatment is essential because mental well-being is deeply intertwined with overall health.
Emotional and Psychological Effects


The emotional ramifications of molluscum contagiosum can be quite complex. Individuals may experience feelings of shame or frustration due to the visible nature of the lesions, which can contribute to negative self-image. It may feel as though one is under a microscope, with the constant worry of being judged or avoided by peers.
Moreover, many patients report anxiety and stress, fearing the possibility of transmitting the virus to others. This often leads to social isolation, as people might refrain from engaging in close relationships or pursuing intimate partners. There is a certain emotional toll that comes when individuals feel they must hide their condition. It breeds discomfort and can cause a vicious cycle where the fear of judgment exacerbates feelings of loneliness.
"A skin condition can be a mirror reflecting our internal conflicts about acceptance and belonging, often more than we realize."
Social Stigma and Consequences
Social stigma is another layer that complicates the experience of those affected by molluscum contagiosum. The association of the virus with a lack of cleanliness or promiscuity can be misleading and harmful. This stigma can lead to ostracism or labeling from others, causing patients to become defensive or fearful in social situations.
As a result, individuals may refrain from discussing their condition openly, which limits their ability to seek support. The silence surrounding their experience often leaves them dealing with the issue alone, magnifying feelings of despair. Also, misinformation about how molluscum contagiosum is transmitted can lead to further discrimination.
In careers, workplaces may not always provide a conducive environment for individuals with visible skin conditions. The risk of being perceived as unprofessional or unclean can influence hiring decisions and workplace dynamics.
To mitigate these issues, education is key. Increasing awareness about molluscum contagiosum—its causes, transmission, and treatment—can help dismantle the surrounding stigma. When society is more informed, the potential for empathy grows, creating a more supportive environment for those affected.
Challenges in Treating Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is not just a viral skin infection; it presents a unique set of challenges that complicate its treatment. Understanding these challenges is crucial for both patients undergoing therapy and professionals guiding them through the options. The resistance to treatment and variability in patient response highlights the need for tailored strategies that consider individual circumstances.
The crux of managing molluscum contagiosum lies in recognizing that no single treatment fits all. Multiple factors influence the treatment process—including patient age, immune status, and even the location of lesions. The focus on these challenges not only provides clarity but encourages a more nuanced approach to treatment planning.
"The approach to molluscum contagiosum treatment is akin to solving a multifaceted puzzle—each piece represents a unique patient factor that must be accounted for in crafting effective care."
Resistance to Treatment
Resistance to treatment is a significant hurdle when managing molluscum contagiosum. Certain therapeutic agents may become ineffective over time, primarily due to the virus's ability to adapt. For instance, topical treatments like Imiquimod can provide robust responses initially, but some patients may find that efficacy diminishes after repeated use. This phenomenon can lead to frustrating cycles, wherein the lesions persist, prompting patients to seek alternatives repeatedly.
Additionally, any underlying conditions like eczema or immunocompromised states can further complicate treatment efficacy. A patient's skin barriers may be less effective, allowing for viral persistence even when treatments appear appropriate. Hence, physicians often explore combination therapies or switch to entirely different modalities based on initial treatment outcomes.
Contributing Factors to Resistance
- Type of Treatment: Certain topical therapies may not penetrate effectively, limiting their action against deeper lesions.
- Patient Compliance: If patients don’t adhere strictly to prescribed regimens, it complicates the assessment of treatment resistance.
- Virus Adaptation: Just as with bacterial infections, the capability of the virus to mutate becomes an important consideration in treatment failure.
It's essential to understand that resistance isn't solely about failure to respond. It can reflect the complex interplay of various biological factors, including immune system interactions. The outcome of treatment often hinges on contextual factors specific to each patient, making resistance a multifaceted issue that doesn't offer a straightforward solution.
Variability in Patient Response
Another key challenge is the variability in how different patients respond to treatments. Even amongst individuals with seemingly similar presentations, the outcomes can differ significantly. This can stem from biological factors such as genetic predispositions, skin type, and individual immune responses. For example, children often experience more standard courses and responses compared to adolescents or adults, who might exhibit more diverse reactions.
The psychosocial background of patients also plays a role in treatment outcomes. Stress levels, mental health, and social support systems can all impact how well an individual responds to treatment. This underscores the importance of a holistic approach, where mental and emotional health are considered alongside physical treatments.
Insights into Patient Variability
- Age and Immune Status: Younger patients might eliminate the virus with fewer complications, reducing treatment times while immunocompromised individuals may struggle longer.
- Treatment Expectations: Patients who have realistic expectations regarding the duration and process of treatment often fare better than those with unrealistic hopes of quick recovery.
- Adherence and Motivation: How motivated a patient is to follow treatment directives profoundly influences their outcomes.
Ending and Future Directions
The realm of molluscum contagiosum treatment is intricate, layered with complexities that reflect both medical challenges and the human experience. As health professionals and researchers strive to fine-tune treatment protocols, it becomes increasingly evident that effective management of this viral skin infection necessitates a multifaceted approach. Explicating the available treatment modalities is essential, particularly when considering their varying efficacies and patient experiences.
One of the key takeaways from our exploration is that there isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. Each patient's unique circumstances, including immune status and co-existing conditions, must be factored into the selection of therapeutic strategies. Moreover, the psychosocial dynamics tied to molluscum contagiosum cannot be overlooked; they play a significant role in shaping a patient’s treatment journey and outcome.
Summary of Effective Treatments
When it comes to tackling molluscum contagiosum, a diverse arsenal of treatments exists. From topical therapies such as Imiquimod and Retinoids to procedural interventions like cryotherapy and curettage, each approach has its own set of benefits and limitations.
- Topical Therapies: Medications like Imiquimod stimulate the immune response, while Retinoids promote skin cell turnover.
- Cryotherapy: By freezing the lesions, this method offers a quick resolution, but it requires trained professionals for safety and efficiency.
- Curettage and Laser Therapy: These are often reserved for persistent cases, providing potentially immediate results.
While these treatments yield varying degrees of effectiveness, understanding individualized patient factors is paramount.
Research Gaps and Future Studies
Despite advancements, significant gaps remain in our knowledge about molluscum contagiosum, especially regarding long-term outcomes and recurrence rates. Future studies ought to prioritize comprehensive prospective trials to gather robust data on:
- Long-Term Efficacy: Tracking treatment outcomes over extended periods could provide insights into the sustainability of various therapies.
- Resistance Mechanisms: A deep dive into potential resistance to treatments, particularly in long-standing cases, might reveal valuable information.
- Cohort Variability: More research is needed on how demographic variables influence treatment success and patient satisfaction.
The journey towards finding optimal treatment pathways for molluscum contagiosum is just beginning. Collaborative efforts in research and clinical practice will enhance our understanding and improve patient care.



