Skin Manifestations of HIV: An In-Depth Exploration


Intro
Understanding the skin manifestations of HIV is essential for healthcare professionals and researchers alike. The skin is often considered a window into the body's overall health, making its conditions particularly relevant in the context of HIV infection. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these manifestations, exploring their underlying mechanisms, clinical presentations, and management strategies. As individuals living with HIV experience various skin issues, recognizing and addressing these problems can significantly enhance patient care and quality of life.
HIV can lead to a range of skin disorders that reflect the immune system's status at different stages of the disease. From early symptoms to late-stage skin-related conditions, these manifestations can provide crucial insights into disease progression. Conditions such as Kaposi's sarcoma, oral thrush, and eczema are just a few examples of how HIV may express itself through the skin.
In this overview, we will look into several key aspects of skin manifestations associated with HIV. This will include discussing relevant research contexts, methodologies, and the implications these conditions have for clinical practice. By enhancing our understanding of these topics, we can better approach the needs of individuals living with HIV.
Prelude
In the context of HIV, skin manifestations are not just ancillary issues but serve as crucial indicators of the patient's overall health. The significance of understanding these skin conditions lies in their potential to reveal the immune status of an individual living with HIV. Many skin disorders arise due to the interplay between the virus, its treatment, and the host's immune response. Moreover, recognizing these manifestations can aid in early diagnosis and successful management of HIV infection.
This article delves into the spectrum of skin conditions associated with HIV, prioritizing a thorough examination of their pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment strategies. An in-depth understanding of these skin manifestations can inform healthcare providers about the varying clinical presentations and importance of timely intervention. By highlighting the connection between skin health and HIV progression, this overview aims to enhance the care provided to patients, ultimately improving their quality of life.
Understanding HIV
HIV, or Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system, specifically the CD4+ T cells, which are vital for immune function. If left untreated, HIV can lead to AIDS, or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, characterized by a severely weakened immune system and increased susceptibility to opportunistic infections.
The virus is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, sharing of needles, or from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding. Over time, untreated HIV leads to progressive immune deficiency, culminating in a range of health complications, including various skin disorders.
Key Features of HIV Infection
- Transmission: Spreads through bodily fluids, particularly blood and sexual fluids.
- Pathogenesis: The virus integrates into the host's DNA, causing immune cell destruction.
- Stages: Includes acute HIV infection, clinical latency, and symptomatic stage leading to AIDS.
Understanding HIV's nature and progression is essential for recognizing its impact on different organ systems, particularly the skin.
Importance of Skin Manifestations
Skin manifestations in individuals with HIV are not merely cosmetic issues. They often reflect underlying immunological deficiencies and can signal the onset of more severe health problems. For clinicians, these symptoms may serve as early warning signs of HIV disease progression or complications. The skin can mirror the immune status of the individual, making it vital to recognize any changes or lesions.
Types of Skin Manifestations
- Dermatitis: Can indicate heightened immune reactivity or secondary infections.
- Fungal infections: Common among immunocompromised individuals, signaling severe immune dysregulation.
- Kaposi's Sarcoma: A malignancy associated with advanced HIV, often presents as lesions on the skin.
By understanding these manifestations, healthcare providers can create tailored management strategies, thus potentially enhancing survival and mitigating complications associated with HIV infection. Skin health is ultimately a critical component of holistic HIV care.
The Epidemiology of HIV-Related Skin Conditions
Understanding the epidemiology of HIV-related skin conditions provides crucial insight into the health landscape of individuals living with HIV. This topic helps highlight the frequency and distribution of skin manifestations that occur with the infection. Recognizing patterns in different segments of the population allows healthcare professionals to develop targeted screening and management strategies. Furthermore, studying these conditions contributes to the overall comprehension of the impact of HIV on skin health and can guide future research initiatives aimed at improving patient outcomes.
Prevalence in Different Populations
The prevalence of skin manifestations in HIV-positive individuals varies across different populations. Studies indicate that people living with HIV often experience a higher incidence of skin conditions compared to the general population. For instance, certain groups, such as men who have sex with men and individuals with a history of substance abuse, tend to exhibit more pronounced skin issues. Other social determinants, including socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and geographical location, also play significant roles in this variation.
Research shows that approximately 90% of patients with advanced HIV or AIDS will experience at least one skin condition in their lifetimes. Conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis or herpes simplex virus infections are among the most commonly reported. Additionally, skin manifestations can serve as early indicators of HIV infection, often surfacing before a definitive diagnosis is made. Therefore, understanding these patterns is critical for early intervention.
Trends Over Time
Over the years, trends in HIV-related skin conditions have evolved significantly, influenced by advances in treatment and changes in the demographics of affected populations. Initially, skin diseases were rampant among those diagnosed with AIDS, largely due to associated immunosuppression. However, with the introduction of antiretroviral therapy, the frequency of severe skin conditions has decreased notably in well-managed patients.
Current trends indicate that while the incidence of certain infections like Kaposi’s sarcoma has diminished, other conditions like psoriasis may be on the rise. This shift may stem from the increase in longevity among individuals receiving effective treatment. As they live longer, they may experience chronic skin conditions more typically associated with aging individuals.
Common Skin Manifestations in HIV
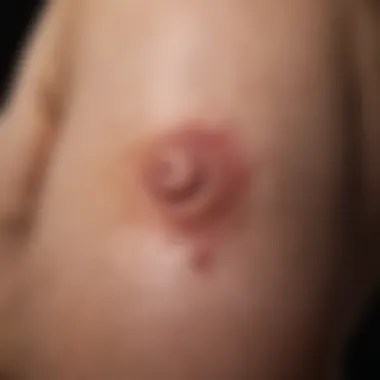

Skin manifestations are often among the first visible signs of HIV infection. They can act as critical indicators of the overall health and immune status of individuals. Early detection of these skin conditions is essential for timely monitoring and management of HIV. Understanding these manifestations helps healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans, thus improving patient outcomes.
Eczema and Dermatitis
Eczema and dermatitis are frequent skin issues faced by those living with HIV. These conditions result in inflammation, redness, and itching. The compromised immune system struggles to fend off irritants and allergens. In many cases, topical corticosteroids are employed for relief. However, managing triggers and applying moisturizers regularly can improve skin health significantly.
Pseudomonas and Folliculitis
Pseudomonas infections, although rare, can appear in individuals with HIV. They typically present with red itchy bumps, often resulting from hair follicle inflammation. This condition is known as folliculitis. It occurs more frequently in patients with advanced HIV. Treatment usually involves topical or oral antibiotics. Patient education on proper hygiene and wound care is also important to prevent these infections.
Psoriasis
Individuals living with HIV may also experience psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition. Psoriasis can cause red, scaly patches on the skin and may worsen with immunosuppression. The emotional and psychological impact of visible psoriasis lesions can affect quality of life. Therapy may include topical treatments, phototherapy, or systemic medications to manage psoriasis effectively.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis often presents as greasy, flaky patches on areas of the body rich in oil glands, like the scalp and face. In HIV-positive individuals, this condition may be more severe and widespread. Treatment involves medicated shampoos or topical antifungals. Maintaining skin hygiene is crucial in mitigating flare-ups.
Kaposi's Sarcoma
Kaposi's sarcoma is a significant concern among people with HIV, particularly in those with AIDS. It appears as dark, purplish lesions on the skin or mucous membranes. This cancer is closely linked to HIV-related immunosuppression. Treatment options vary, depending on the extent of the disease, and may include chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Herpes Zoster
Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, can have a more severe course in HIV-infected individuals. The reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus results in painful blisters and rash. Antiviral medications like acyclovir can help; pain management is also important. Vaccination for individuals with well-controlled HIV can help prevent herpes zoster.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are common in individuals with compromised immune systems. These infections can manifest in various forms, including candidiasis and tinea. They often require antifungal treatments, either topical or systemic, depending on severity. Education on skin care and hygiene can prevent recurrent infections.
Skin manifestations offer a window into the health of individuals with HIV. Recognizing and understanding these conditions can improve care and management strategies.
Pathophysiology of Skin Manifestations in HIV
Understanding the pathophysiology of skin manifestations in HIV is pivotal for recognizing how the virus affects the body. These skin changes are not merely superficial; they reflect deeper immunological disruptions. The intricate relationship between HIV and the skin is a window into the overall health of an individual living with the virus. Moreover, these manifestations often serve as early signs of a declining immune system, which makes their study crucial for timely intervention and management.
Role of Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression plays a central role in the development of skin conditions in HIV patients. As the virus progresses, it compromises the immune response, leading to increased vulnerability to infections and skin diseases. The depletion of CD4 T-cells, a hallmark of HIV infection, significantly undermines the body's ability to ward off opportunistic pathogens. This results in a range of skin issues, from common infections like herpes and fungal infections to more serious conditions, such as Kaposi’s sarcoma.
The weakened immune system means that even typically harmless microorganisms can cause significant skin issues. For instance, fungal infections may become more prevalent among patients. At the same time, inflammatory skin conditions such as psoriasis may be exacerbated due to immune dysregulation. Understanding this process is vital for healthcare providers to effectively manage and anticipate the skin-related challenges faced by their patients.
"Skin manifestations can indicate an underlying condition, often reflecting the immunological status of individuals living with HIV."
Viral Influence on Skin Health
The direct effects of HIV on skin health are also significant. The virus can induce alterations in skin cell function and disrupt the normal skin barrier. Research indicates that HIV can lead to conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis through multiple pathways, including inflammation and alterations in lipid metabolism. Notably, the upregulation of certain cytokines and chemokines can exacerbate these skin issues.
Additionally, the role of co-infections complicates the landscape of skin health in HIV patients. Many individuals with HIV also suffer from other viral infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), which can further worsen skin manifestations. The interplay between HIV and other pathogens drives a vicious cycle of skin issues, leading to a decline in patients' quality of life.
Diagnosis of Skin Manifestations Related to HIV
The diagnosis of skin manifestations related to HIV plays a critical role in managing and understanding this complex virus. Skin conditions often act as early indicators of HIV infection or progression, making their identification essential for timely intervention. Each skin manifestation can provide insight into the patient’s immune status and overall health, thereby guiding treatment decisions.

An accurate diagnosis not only assists healthcare professionals in determining the severity of HIV infection but also enables the implementation of appropriate therapeutic strategies. This proactive approach can effectively reduce morbidity and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Thus, understanding the clinical features and conducting thorough assessments are vital components in the diagnostic process.
Clinical Assessment
Clinical assessment involves gathering detailed patient histories and performing physical examinations. Healthcare providers should pay particular attention to skin changes, noting patterns and characteristics of lesions, as these can significantly differ based on the underlying condition. Common manifestations may include:
- Eczema: Often presents as itchy, red patches that can appear all over the body.
- Psoriasis: Characterized by thickened, red patches with silvery scales.
- Kaposi's Sarcoma: Identified as lesions that can appear anywhere, often purple or brown in color.
A thorough examination also requires understanding the patient's medical history, including previous skin issues, medication use, and current health status. Notably, some patients might be more predisposed to certain skin conditions due to their immune profile.
Moreover, practitioners often need to differentiate between various skin disorders, which can complicate the clinical picture. The clinician should evaluate not only the skin but also the patient’s systemic symptoms, as multiple conditions may coexist in individuals with HIV.
Laboratory Testing
Laboratory testing complements clinical assessment. It helps confirm diagnoses and rule out other conditions. Key tests include:
- Skin biopsy: This allows for histopathological examination, providing a definitive diagnosis. Abnormal cellular features can indicate specific conditions, such as Kaposi's Sarcoma or herpes zoster.
- Serological tests: These may assess for secondary infections or conditions that may simultaneously affect the skin.
- Culture tests: Microbial cultures can identify specific pathogens responsible for infections, such as fungi or bacteria.
Utilizing laboratory testing enhances diagnostic accuracy. It ensures that healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans effectively. It is also important to recognize that some skin conditions may respond differently to treatment based on laboratory findings. Combining clinical assessment with laboratory testing creates a comprehensive framework for understanding and managing skin manifestations related to HIV.
Management Strategies for Skin Conditions in HIV Patients
Managing the skin conditions associated with HIV is vital for improving the overall quality of life of affected individuals. These skin manifestations can indicate the progression of the disease as well as the effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy. Addressing these conditions requires a comprehensive strategy that integrates different treatment modalities and considers the specific needs of each patient.
The benefits of effective management strategies are manifold. Not only do they alleviate physical symptoms, but they also play a significant role in enhancing the psychological well-being of patients. Skin disorders can lead to social stigma and reduced self-esteem, impacting day-to-day interactions. Therefore, a focused management approach can help reduce these psychosocial burdens while also improving adherence to HIV treatment.
Additionally, it is important to recognize the interplay between skin health and immune function. Maintaining healthy skin can support bodily defenses and reduce the likelihood of infections. Understanding these considerations leads to more holistic healthcare for individuals living with HIV.
Overall, an effective management strategy for skin conditions should encompass topical treatments, systemic therapies, and interdisciplinary care approaches to ensure comprehensive patient support.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first-line approach for managing skin conditions in HIV patients. These treatments typically involve the direct application of medications to the skin. Common topical agents include corticosteroids, antifungals, and emollients, depending on the specific skin issue being addressed.
Corticosteroids can effectively reduce inflammation and itching in dermatologic conditions like eczema and psoriasis. Antifungal creams are essential for managing fungal infections that may arise due to compromised immune systems. Emollients help maintain skin hydration and barrier function, which is critical for all patients.
When applying these treatments, it is essential to recognize the individual response. Dosage and method of application can significantly influence efficacy. Regular monitoring of the patient's skin condition is crucial for adjustments to the treatment plan.
Systemic Therapies
Systemic therapies may be necessary for more severe skin manifestations or when topical treatments fail. These therapies involve the use of medications that have systemic effects on the body. Options include oral antifungals, antibiotics, or immunosuppressive drugs, depending on the condition.
For instance, oral antibiotics may be warranted for severe forms of folliculitis or bacterial skin infections, while systemic antifungals can treat extensive fungal infections. In cases of inflammatory skin conditions or severe psoriasis, immunosuppressive medications might be considered.
These therapies require careful monitoring due to potential side effects. Regular follow-ups help in assessing the response to treatment while managing any adverse reactions that may arise.
Interdisciplinary Care Approaches
An interdisciplinary care approach is essential for providing comprehensive management of skin conditions in HIV patients. This strategy involves collaboration among various healthcare professionals, including dermatologists, infectious disease specialists, primary care providers, and mental health professionals.
Coordination among these specialists ensures all aspects of a patient's health are attended to. For example, dermatologists can focus on specific skin issues, while HIV specialists manage overall viral load and immune status. Mental health professionals help address the psychological impacts of visible skin disorders, providing patients with valuable coping strategies.
This integrated model fosters better communication, improves patient outcomes, and enhances a patient’s overall experience within the healthcare system. As skin conditions are often a reflection of underlying health issues, attending to them within a broader framework remains paramount.


"Holistic management of skin conditions in HIV patients not only addresses physical concerns but also bolsters emotional and social health, thus improving quality of life."
Psychosocial Considerations
The psychosocial dimensions of skin manifestations in HIV are often overlooked but play a crucial role in the overall health and well-being of affected individuals. Skin conditions can significantly impact a person's self-esteem and social integration. Therefore, understanding these considerations is essential in managing HIV effectively. Acknowledging the interplay between psychological and social factors allows for a more holistic approach to treatment.
Impact of Skin Conditions on Quality of Life
Skin manifestations can lead to considerable distress for individuals living with HIV. The visibility of skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and Kaposi's sarcoma can result in feelings of embarrassment and stigma. This can decrease the individual’s quality of life substantially. People might withdraw from social activities, leading to isolation. Key areas affected include:
- Emotional Well-Being: Individuals often experience anxiety and depression due to visible skin lesions. This is further compounded by the stigma associated with HIV.
- Social Relationships: The visible nature of skin conditions can create barriers to forming and maintaining relationships. Fear of judgment can lead to withdrawal and reduce social support, which is vital during challenging times.
- Employment Opportunities: For some, skin manifestations may affect job performance or the ability to seek employment. Discrimination in the workplace based on appearance is a concern, potentially leading to financial stress and decreased quality of life.
Effective management of these skin issues involves not only addressing the physical symptoms but also providing psychological support. This allows for improved emotional health and greater overall well-being.
Support Mechanisms for Affected Individuals
Support for individuals with HIV and skin manifestations involves a multifaceted approach. The following strategies can be beneficial:
- Psychological Counseling: Individual therapy or support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of living with visible skin conditions. This promotes resilience and emotional strength.
- Education and Awareness: Enhancing awareness about HIV and its skin manifestations within the community can help reduce stigma. Education encourages understanding and acceptance, mitigating feelings of isolation.
- Peer Support Programs: Connecting individuals with similar experiences fosters community support. These connections can provide invaluable emotional assurance and practical advice.
- Access to Dermatological Care: Timely consultations with dermatologists experienced in managing HIV-related skin conditions can aid in effective treatment, improving both symptoms and psychological outcomes.
By adopting comprehensive support mechanisms, healthcare providers can address the psychosocial needs of individuals with HIV effectively. This approach ultimately contributes to a more favorable quality of life.
Future Directions in Research
Research on skin manifestations associated with HIV holds significant importance as it can lead to better understanding and management of these conditions. Investigating new therapeutic methods and improving diagnostic accuracy can substantially enhance patient outcomes. As HIV continues to evolve, it is crucial to gather insights in order to address the changing landscape of skin-related health issues in affected individuals.
Novel Therapeutic Approaches
Current treatments for skin conditions related to HIV can sometimes be insufficient due to varying factors like individual immunity and the unique response of skin to infections or irritations. Thus, novel therapeutic approaches are essential to replenish the existing treatment arsenal. Recent studies have explored the use of biologic drugs that target specific immune pathways, potentially driving better outcomes for patients suffering from skin manifestations.
Additionally, the development of topical agents specifically formulated for HIV-infected skin could provide relief from common skin issues such as eczema or dermatitis. Ongoing clinical trials examine compounds derived from natural sources, such as plant extracts, which exhibit antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. Such approaches not only aim to treat the symptoms but also target the underlying causes of skin conditions in HIV patients.
Advancements in Diagnostic Techniques
Advancing diagnostic techniques are critical for early detection and appropriate management of skin conditions in patients with HIV. Traditional methods often rely on clinical visible signs and may lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment. The integration of molecular methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can enhance diagnostic accuracy by identifying specific pathogens implicated in skin diseases.
Moreover, the implementation of non-invasive imaging technologies like optical coherence tomography (OCT) offers a promising future for dermatological diagnostics. These techniques can provide detailed insights into skin structures and help differentiate between various skin conditions. Additionally, utilizing machine learning algorithms to analyze dermatological images may lead to earlier recognition of skin manifestations related to HIV, facilitating timely interventions.
Advancements in diagnostic techniques can significantly improve the management of HIV-related skin conditions, ensuring that patients receive precise and effective treatment regimens.
The ongoing research is vital for addressing the complex interactions between the HIV virus and skin health. By fostering innovative therapeutic strategies and refining diagnostic tools, researchers can make significant contributions to the overall care of individuals living with HIV.
Ending
The conclusion of this article holds significant weight, as it synthesizes the multifaceted aspects of skin manifestations related to HIV. These manifestations are not just superficial concerns; they provide critical insights into the overall health of individuals living with HIV. Understanding these aspects can significantly enhance the management and treatment protocols for affected patients.
Summary of Key Findings
Through this exploration, we have uncovered that skin conditions frequently seen in HIV patients range from common ailments like eczema and dermatitis to more serious issues such as Kaposi's sarcoma. Each condition has its own pathophysiology, influenced by the immunocompromised state of individuals with HIV. Regarding prevalence, certain populations demonstrate a higher incidence of specific skin conditions. Moreover, HIV-related skin manifestations act as essential markers for assessing disease progression. Recognizing this link emphasizes the importance of continuous skin assessment in patient care.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The practical implications of these findings are substantial. Clinicians must include routine evaluations of skin conditions in their assessments of HIV patients. Early detection can lead to timely interventions, reducing morbidity associated with these skin conditions.
Moreover, a multidisciplinary approach must be employed, integrating dermatologists, immunologists, and mental health professionals. This collaboration can improve the quality of life for patients, addressing both physical and psychosocial aspects of their health. Education on the significance of skin manifestations for patient and healthcare provider alike is essential. Awareness can drive better outcomes and foster a supportive environment for individuals navigating the complexities of living with HIV.
"Understanding skin manifestations is crucial. It is not just about treatment; it's about comprehensive care."
By focusing on these elements, healthcare providers can significantly influence the management and quality of life for individuals living with HIV.



