Understanding the Lupus Rash: Diagnosis and Management

Intro
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is known for its wide array of symptoms, among which the lupus rash is particularly significant. This skin manifestation can vary greatly in appearance and impact, making its understanding crucial for effective management. As this article explores, the lupus rash can serve as a diagnostic marker and has profound implications for a patient’s quality of life. The following sections will delve into the characteristics of the lupus rash, its diagnosis, and various management strategies.
Research Context
Background and Rationale
The lupus rash is a cutaneous manifestation that can vary in type, including the hallmark butterfly rash and other skin lesions. Understanding these types aids in recognizing the disease’s complexity and the variations that exist among individuals. There is a need to enhance awareness about how the rash presents and what it signifies in the context of SLE.
Researching the lupus rash is important in providing better care for patients. Healthcare professionals must be well-informed about its characteristics and implications since early detection and management can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Literature Review
A review of existing literature reveals the nuanced presentation of lupus rashes among the SLE population. Multiple studies have highlighted that the rash may not only affect physical health but also emotional and psychological well-being. For instance, Haller et al. (2021) noted that patients experienced higher levels of anxiety and depression correlated with visible skin lesions.
Additionally, researchers have documented diverse therapeutic approaches. Topical corticosteroids have been widely recommended, although broader immunosuppressive therapies are also common depending on severity. The findings emphasize the need to consider both clinical symptoms and the lived experience of patients.
Methodology
Research Design
This article relies on a qualitative approach, combining literature synthesis and case study analysis. Reviewing peer-reviewed articles, meta-analyses, and clinical guidelines provides a holistic view of the subject. The focus is on consolidating findings that inform about characteristics, diagnosis, and management of the lupus rash.
Data Collection Methods
Data for this article were gathered from various sources, including:
- Peer-reviewed journals
- Clinical guidelines from organizations like the American College of Rheumatology
- Patient testimonials from health forums like reddit.com
- Recent surveys from SLE patient data
By employing reliable methods of collection, the article aims to present a well-rounded representation of what is known today about the lupus rash.
"Understanding the characteristics of a lupus rash improves diagnostic accuracy and patient experience."
The subsequent sections will further elaborate on the specific characteristics of the lupus rash, diagnostic criteria, and effective management strategies.
Defining the Lupus Rash
Understanding the lupus rash is essential in the context of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The lupus rash serves not only as a physical manifestation of this chronic autoimmune disease but also as an indicator of the underlying pathological processes involved in SLE. By defining the lupus rash clearly, healthcare professionals can improve diagnostic accuracy, enabling timely intervention and management strategies that significantly enhance patient outcomes. Moreover, raising awareness about the characteristics and implications of lupus rashes can lead to better support for affected individuals.
Overview of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by a dysregulated immune response. In this condition, the body inadvertently targets its own tissues, leading to inflammation and damage in various organs. The onset of SLE can vary significantly between individuals, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe.
SLE can impact any organ system, but the skin is one of the most commonly affected areas. Here, the lupus rash is a prominent feature, often serving as one of the first physical signs prompting evaluation for the disease. Its presence raises specific concerns regarding disease activity and potential flares, making understanding these rashes crucial for effective health management.
What is a Lupus Rash?
A lupus rash refers to any skin manifestation observed in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. These rashes can take multiple forms, each distinct in appearance and implications.
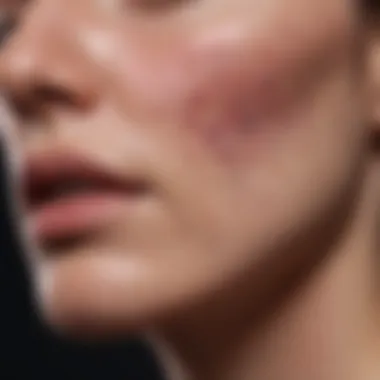
The malar rash, often referred to as a butterfly rash, is characterized by redness across the cheeks and nose, resembling a butterfly shape. This specific rash holds significant diagnostic value as it is highly indicative of SLE. Another common type is the discoid rash, which presents as raised, scaly patches often found on sun-exposed areas of the skin.
Additionally, patients may experience photosensitive rashes that worsen with sun exposure, highlighting the importance of sun protection in management strategies.
The characteristics of lupus rashes can vary widely. Therefore, accurate identification is critical for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Determining the nature of a lupus rash helps guide further investigation and management, ultimately providing better care for individuals affected by this condition.
Types of Lupus Rashes
Understanding the different types of lupus rashes is crucial for accurately diagnosing and managing systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Each type can present unique characteristics and implications for a patient’s health. Recognizing these rashes can aid healthcare providers in making informed decisions regarding treatment strategies, as well as facilitate better patient education. Furthermore, awareness of these distinct rash types helps in identifying potential triggers and developing personalized management plans. In general, the lupus rash not only affects the skin but can also reflect the underlying immune dysfunction present in SLE.


Malar Rash
The malar rash is one of the hallmark manifestations of lupus. It appears as a butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and the bridge of the nose. This rash may be mildly raised and is typically red or erythematous. Patients often report that the rash worsens with sun exposure, which is a common trigger for many lupus symptoms. It can serve as an indicator of disease activity, and its presence may suggest involvement of systemic inflammation.
Clinically, the malar rash can vary greatly in severity among patients, sometimes disappearing on its own and returning during flare-ups. Educating patients about potential triggers and providing guidance on sun protection is essential. It is important to note that while the malar rash is strongly associated with lupus, it is not exclusive to it, leading to possible misdiagnosis in some cases.
Discoid Rash
Discoid rash is another common type of lupus rash. Unlike the malar rash, discoid lesions are circular and scaly, often found on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, and scalp. They can appear as red or purple plaques and may cause scarring or changes in skin pigmentation over time. Discoid lupus erythematosus can occur independently of SLE and may exist as an isolated condition.
The chronic nature of discoid rashes can be distressing for patients. It is essential to discuss the various treatment options available for managing these lesions, including topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators. Patients need to be informed about the possibility of the rash becoming worse if they do not take preventive measures against sunlight and skin damage.
Photosensitive Rash
Photosensitive rash is a reactive condition that occurs in response to ultraviolet light exposure. Patients with lupus often experience exacerbation of skin rashes following sunlight exposure. This rash can appear in various forms, including erythema, urticaria, or vesicles, depending on individual skin sensitivity.
Recognizing photosensitivity is vital for patients’ self-management. Patients should be educated about sun safety practices, such as wearing protective clothing and using high-SPF sunscreen. Implementing a proactive approach can minimize the frequency and severity of these rashes.
Other Dermatologic Manifestations
In addition to the commonly recognized rashes like the malar and discoid, SLE can lead to other dermatologic manifestations. These include lesions that resemble acne, hair loss, and vasculitis, presenting as red or purplish spots. Some patients may also encounter changes in nail health, leading to brittleness or discoloration.
The diversity of skin-related symptoms underscores the importance of comprehensive evaluations. Healthcare providers should remain vigilant for unusual presentations and collaborate with dermatologists if needed. Monitoring and addressing the overall dermatological health can contribute significantly to improving quality of life for patients with lupus.
Understanding the diversity of lupus rashes is essential for both clinicians and patients in managing the complex nature of this autoimmune condition.
Clinical Characteristics of the Lupus Rash
Understanding the clinical characteristics of the lupus rash is essential for effective diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The rash presents itself in various forms and often serves as a pivotal indicator of the disease. Recognizing the specific elements of the rash can lead to timely interventions and a better quality of life for patients. Furthermore, an understanding of the clinical characteristics helps healthcare providers formulate individualized treatment plans based on the presentation of the rash and associated symptoms. Thus, this section aims to elaborate on the visual appearance, common locations, and associated symptoms of lupus rashes, providing a thorough insight into their significance.
Visual Appearance
The visual appearance of a lupus rash can be diverse, manifesting distinctly based on the type and the individual. The most recognized type, the malar rash, often appears as a butterfly-shaped erythematous lesion on the cheeks and nose. This rash is typically well-defined and can also present with a scaly texture. In contrast, discoid rashes are characterized by round, raised lesions that may have a thick crust. They can lead to scarring if not managed properly. Photosensitive rashes arise as a consequence of sun exposure, leading to similar lesions on sun-exposed areas such as the face, neck, and arms. The variability in appearance can sometimes complicate diagnosis, making it crucial for medical professionals to be vigilant and knowledgeable about these distinctions.
Common Locations
Lupus rashes are often observed in particular areas of the body. The malar rash predominately appears on the face, typically across the cheeks and nose. Discoid rashes frequently develop on the scalp, ears, and other sun-exposed areas. They can appear as circular, inflamed patches, sometimes leading to hair loss if they affect the scalp. Photosensitive rashes can be seen on the upper body, arms, and back, where UV exposure is common. The specific localization of these rashes often correlates with the underlying pathophysiology and can provide vital information for diagnosis.
Proper identification of the lesion's location can aid clinician in recognizing the severity and possible complications associated with lupus rash.
Associated Symptoms
Alongside the distinct visual characteristics, lupus rashes often present with associated symptoms that contribute to the patient's overall clinical picture. Common symptoms include itching, burning, and tenderness around the areas of the rash. Some patients may also experience systemic symptoms like fatigue, fever, and joint pain. The coexistence of these symptoms highlights the multisystem nature of lupus and reinforces the need for a holistic approach in both diagnosis and management. Recognizing these additional signs can help healthcare providers monitor disease activity and adjust treatment strategies as needed.
In summary, the clinical characteristics of the lupus rash encompass important aspects of visual appearance, common locations, and associated symptoms. Highlighting these elements provides critical insights into the effective diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Pathophysiology of Lupus Rashes
Understanding the pathophysiology of lupus rashes is crucial in comprehending the broader implications of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The lupus rash results from complex interactions between various immune system components, genetic factors, and environmental triggers. This section will elucidate these mechanisms, which will help both patients and healthcare providers improve diagnosis and management strategies.
Immune System Dysfunction
The immune system in individuals with lupus does not function as it should. Instead of only attacking pathogens, it mistakenly targets healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and damage. This autoimmune response contributes significantly to the development of lupus rashes.
The role of autoantibodies is important in this dysfunction. These antibodies attack the body’s own cells, causing an inflammatory reaction. In particular, the presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANAs) is common in individuals with SLE. These antibodies can bind to skin cells, activating complement pathways that contribute to the inflammatory process.
Additionally, the dysfunction in T-cells, especially regulatory T-cells, is notable. Regulatory T-cells usually help moderate immune responses. When these cells are impaired, there is an overactive immune response, which can aggravate skin lesions characteristic of lupus rashes.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetics also play a vital role in the pathophysiology of lupus rashes. Certain genetic markers have been identified that increase the susceptibility of an individual to develop SLE and its associated skin conditions. The most studied genetic factors include polymorphisms in the complement component and various cytokine genes.


There is a tendency for lupus to run in families, indicating that individuals with a family history of the disease have a higher likelihood of developing similar symptoms. However, it’s important to recognize that while genetics contribute to risk, the interaction with environmental factors is equally essential in triggering the disease.
"Understanding the genetic basis of lupus can help in identifying at-risk populations and developing personalized therapeutic strategies."
Diagnosis of the Lupus Rash
The diagnosis of the lupus rash is crucial in understanding systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Accurate diagnosis not only forms the foundation for effective management but also aids in differentiating lupus rashes from other skin conditions. Timely diagnosis can prevent complications, improve patient outcomes, and empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Clinical Evaluation
Clinical evaluation is an essential step in diagnosing lupus rash. A healthcare provider begins by taking a detailed medical history, which helps identify any previous occurrences of lupus or related symptoms. Patients are often asked about family history, medication use, and any recent illnesses. A physical examination follows, with the physician focusing on skin lesions. Key characteristics to evaluate include:
- Appearance: Is the rash distinctive? Typical lupus rashes, such as the malar rash, often have a specific appearance that sets them apart from other dermatologic issues.
- Distribution: Where are the rashes located on the body? Certain rashes are known to appear in particular areas, such as the face, scalp, and upper body.
- Symptoms: Patients may experience itching, burning, or other discomfort associated with rashes, which can play a role in evaluating their severity and impact on the patient's quality of life.
Through careful observation and communication, clinicians can form a preliminary assessment of whether the skin changes may be consistent with a lupus rash.
Diagnostic Tests
After the clinical evaluation, diagnostic tests help confirm the presence of lupus and rule out other conditions. Several tests can be utilized:
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test: A common screening test for autoimmune diseases. While a positive result may not be specific to lupus, it can indicate the need for further investigation.
- Anti-double-stranded DNA Antibody Test: This test measures specific antibodies associated with SLE and is more directly linked to lupus.
- Complement Levels: A blood test that measures proteins involved in the immune response. Decreased levels may indicate active lupus.
- Skin Biopsy: In some instances, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the exact nature of the rash and rule out other dermatologic diseases.
The combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests enables a comprehensive understanding of the patient's condition, paving the way for proper management.
"Understanding the diagnostic process is essential for effective lupus management, as it directly influences treatment options and outcomes."
Through this layered approach to diagnosis, healthcare providers can deliver tailored treatment strategies that align with the individual needs of lupus patients.
Management Strategies for Lupus Rash
Managing the lupus rash is crucial for improving the quality of life for affected individuals. This approach involves not only treating the rash itself but also addressing underlying factors contributing to its persistence. Effective management strategies can help mitigate the symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and enhance the overall wellbeing of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Medications
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments play a significant role in managing lupus rashes. These treatments often involve the application of creams, ointments, or gels directly to the affected skin areas. A key characteristic of topical treatments is their localized effect. This allows for direct targeting of rashes without systemic side effects. Common options include corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. These medications can reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
One of the unique features of topical treatments is their ease of use. Patients can apply them at home, which ensures greater adherence to treatment. However, possible disadvantages include limited effectiveness for widespread rash or rashes that are very deep. Some patients may also experience thinning of the skin with prolonged use of topical steroids.
Systemic Therapy
Systemic therapy is another critical component in the management of lupus rashes. This type of treatment involves medications that affect the entire body. Common choices include antimalarials like hydroxychloroquine and immunosuppressants like azathioprine. A key characteristic of systemic therapy is its ability to address the underlying autoimmune processes, providing broader control over lupus symptoms, including skin manifestations.
A unique feature of systemic therapy is its long-term effects. Unlike topical treatments that may only provide temporary relief, systemic medications can help prevent future flare-ups of the rash. However, they come with potential disadvantages, such as the risk of side effects affecting other organs. Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is essential to ensure safety during treatment.
Lifestyle Modifications
Sun Protection
Sun protection is a vital lifestyle modification for individuals with lupus rash. Ultraviolet (UV) light is known to trigger or exacerbate skin lesions in many patients. A key characteristic of sun protection is the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens that filter both UVA and UVB rays. This approach is particularly beneficial as it can significantly reduce the incidence of flare-ups, allowing individuals to engage more fully in outdoor activities without fear of causing skin damage.
The unique feature of sun protection is that it’s manageable and can be tailored to individual preferences. Wearing protective clothing and seeking shade are additional strategies that promote skin health. The main disadvantage might be the limitation on outdoor exposure, which some might find challenging or restrictive. However, the benefits often outweigh these concerns in overall health.
Skin Care Regimens
Skin care regimens represent another essential aspect of managing lupus rashes. A proper regimen involves gentle cleansing and moisturizing of the skin to maintain its barrier function. A key characteristic of skin care regimens is their emphasis on using hypoallergenic and fragrance-free products to avoid irritation. This approach is beneficial as it directly mitigates dryness and improves skin appearance and comfort.
A unique feature of effective skin care regimens is their flexibility. Patients can modify routines based on changes in skin condition. However, careful selection of products is crucial, as some may worsen symptoms. The importance of individualized care cannot be overstated in ensuring the best outcomes for those with lupus rash.
Impact on Quality of Life

The impact of lupus rash on quality of life is a significant aspect to consider when discussing systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Patients suffering from lupus often face various challenges, and the presence of a rash can substantially affect their daily lives. The visibility of the rash, often located on the face and other parts of the body, can lead to self-consciousness and emotional distress. This is particularly relevant for individuals who might prioritize physical appearance due to personal, cultural, or social factors.
Several elements contribute to the overall quality of life of lupus patients:
- Self-Esteem: The visible nature of a lupus rash can lead to feelings of embarrassment or shame. Many individuals struggle with their self-image, which can decrease their confidence when engaging in social or professional activities.
- Emotional Well-Being: Chronic skin conditions often correlate with psychological issues, such as anxiety and depression. The presence of a rash can exacerbate these feelings, complicating the emotional landscape for individuals with lupus.
- Social Interactions: The psychological effects often extend to social implications. Patients may withdraw from social activities as a means of coping with the negative perceptions of their appearance. This can lead to isolation and a diminished support system, which is critical for managing a chronic illness like lupus.
"Quality of life is not merely the absence of disease, but the presence of overall well-being."
In addressing the impact of lupus rash on quality of life, it becomes essential to implement management strategies that not only treat the physical symptoms but also enhance emotional and social well-being. By focusing on these areas, healthcare providers can facilitate a more holistic approach to patient care, ensuring that individuals with lupus live fulfilling lives despite the challenges presented by their condition.
Psychological Effects
Psychological effects of lupus rash are intertwined with its visibility. Patients frequently experience anxiety and depression linked to their rash. This psychological burden can create a cycle where the emotional distress exacerbates the physical symptoms and vice versa.
The mental strain can also lead to an increased sense of vulnerability. The uncertainty regarding flare-ups and their effect on appearance can cause significant distress. Support systems, such as therapy or support groups, can be beneficial.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This therapy helps patients develop coping strategies to manage their response to the rash and its impact on their lives.
- Peer Support: Engaging with others who understand the situation can lessen feelings of isolation.
Social Implications
Social implications of a lupus rash are profound. Interaction with peers and society can become daunting. Patients may avoid gatherings or public places to prevent unwelcome attention or judgments on their appearance.
The fear of stigma is real. They might feel marked by their condition, which can lead to withdrawal from relationships or social opportunities. Understanding from friends and family, alongside societal education on lupus, can help mitigate these effects.
- Education and Awareness Programs: These programs can raise awareness and foster a more accepting environment for those affected by lupus.
- Advocacy Efforts: Encouraging advocacy efforts can challenge misconceptions and provide support avenues for those suffering from lupus.
Considering both the psychological and social implications, it's crucial to address the multifaceted nature of living with lupus rash. Care strategies must prioritize mental health and social engagement to improve the overall quality of life for those affected.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Exploring the lupus rash's emerging research is essential for understanding how this condition keeps evolving. Scientists and medical professionals are dedicated to finding better management strategies and treatment pathways, providing patients with more effective options. Identifying and understanding advancements in disease management can lead to improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
Advances in Treatment Approaches
Lupus, being an unpredictable disease, often requires novel treatment approaches. Recent studies focus on targeting specific pathways in the immune system, attempting to minimize flare-ups and improve skin manifestations. New drug therapies such as belimumab have shown promise in controlling systemic lupus erythematosus and, consequently, its associated rashes. Researchers are also investigating the potential of biologic treatments that target underlying immune dysfunction in more selective ways.
Additionally, advancements in photoprotection highlight a growing trend in managing lupus rashes, especially in patients with photosensitivity. Innovations in broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing can play a crucial role in preventing skin lesions. In essence, the continuing development of comprehensive treatment plans, combining pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches, signifies a shift towards more patient-centered care.
Potential Role of Biomarkers
Biomarkers represent a promising frontier in lupus research, offering insights into disease activity and treatment response. Identifying specific biomarkers can help predict flare-ups and provide tailored therapeutic strategies. For instance, researchers are investigating various cytokines and autoantibodies linked to lupus flare triggers. If successfully utilized, these biomarkers can allow for proactive management rather than reactive treatment.
Furthermore, biomarkers can enhance the diagnostic process. They have the potential to differentiate between various types of lupus and severity levels. This specificity can lead to a more precise approach to treatment, reducing trial and error in medication selection.
"The future of lupus management may lie significantly in biomarker research, enabling clinicians to tailor treatments based on individual disease profiles."
Advancements in this area underscore the importance of continuous research, emphasizing the need for incorporating biomarker studies into routine patient care. Overall, the focus on emerging research is vital in enhancing understanding and treatment approaches to manage the complexities of lupus rash effectively.
Closure
The conclusion serves a critical role in synthesizing the key components discussed throughout the article, emphasizing the profound importance of the lupus rash in the context of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Understanding the characteristics, diagnosis, and management of this condition is vital not only for healthcare professionals but also for patients diagnosed with lupus. The lupus rash is often among the first indications of SLE, making its recognition paramount in clinical settings.
With a clear grasp of the different types of lupus rashes and their clinical manifestations, stakeholders can make informed decisions on diagnostic approaches. The implications of the rash extend beyond mere physical symptoms; they can significantly affect patients' quality of life, including psychological and social well-being. By reinforcing the knowledge of lupus rash among medical practitioners and the general public, increased attention can lead to timely interventions and improved treatment outcomes.
Additionally, the management strategies outlined are essential to ensure effective patient care. They provide a framework for addressing common challenges faced by individuals living with this condition. In summary, this article illuminates the multifaceted nature of the lupus rash and its implications on patient life, acting as a valuable resource for those involved in lupus care.
Recap of Lupus Rash Importance
The lupus rash is a defining characteristic of systemic lupus erythematosus and serves as a visual clue for diagnosis. It may appear in varying forms, including the well-known malar rash, which is often seen on the face. Recognizing these manifestations is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention, ultimately leading to better management of the disease. This awareness can make a considerable difference in patient outcomes and their overall treatment journey.
Call for Increased Awareness and Research
There is a pressing need for heightened awareness regarding the lupus rash and its implications. This awareness can lead to better training for healthcare providers to identify and manage lupus effectively. Furthermore, ongoing research is essential to explore new diagnostic tools, treatment options, and support mechanisms for patients. Investments in research can pave the way for breakthroughs that enhance understanding of the underlying mechanisms of lupus and its various skin manifestations.
Promoting education and support for those affected by lupus is equally critical. Creating resources that facilitate discussions about the challenges faced by patients can help normalize the experiences of living with this condition. Engaging individuals in research participation also offers an opportunity to advance scientific knowledge and improve care practices in this area.
"Increased understanding and awareness can significantly elevate the standard of care for lupus patients, ensuring their voices are heard and needs addressed."



